Search: 4362 news
-
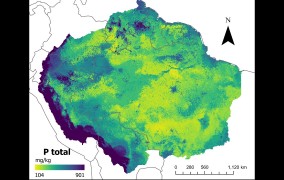
Maps developed with artificial intelligence confirm low levels of phosphorus in Amazonian soil
2024-04-29Research introduces new methodology to describe the amount of the mineral, which is important in the growth cycle of vegetation and can affect the forest’s response to climate change. -
Theories that explain the crisis in democracy are inadequate for Latin America, experts say
2024-04-24Countries in the region are experiencing a different phenomenon from that observed in the United States and Europe, where increased social inequality may have been the cause of the advance of political polarization. The assessment was made by participants in FAPESP Week Illinois. -
Researchers test new behavioral health interventions
2024-04-24Group from the University of Illinois in Chicago creates program to stimulate math learning through physical activity; results of the work were presented at FAPESP Week Illinois. -
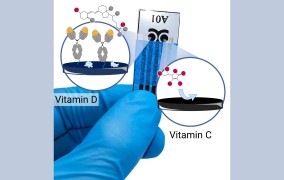
Bioelectronic chip detects vitamins C and D in saliva in under 20 minutes
2024-04-24The device was developed at the University of São Paulo and can be used for self-monitoring of micronutrients, assistance with personalized diets, and prevention of deficiencies and toxicity. -
Study confirms effectiveness of bivalent COVID-19 vaccine
2024-04-24Brazilian scientists conducted the first research project to evaluate the immunity induced in an actual group of vaccinated subjects. Their findings are reported in the Journal of Medical Virology. -
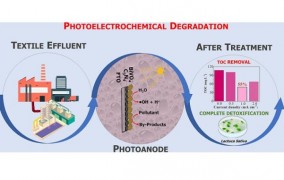
Light-activated materials perform well in treatment of textile effluent
2024-04-24Investigators affiliated with two FAPESP-supported research centers conducted an experiment using actual effluent from the textile industry. The results are detailed in the journal Chemosphere. -
Technology for local production of industrial enzymes in Brazil
2024-04-24A startup supported by FAPESP is developing a platform that will enable local production of enzymes to act as catalysts for chemical reactions. -
Food insecurity is significant among inhabitants of the region affected by the Belo Monte dam in Brazil
2024-04-24A study of 500 households in Altamira, a city near the dam in Pará state, showed that 61% experienced food insecurity. -
Without proper management, Cerrado becomes disfigured and less resilient to climate change
2024-04-22A study conducted over a period of 14 years in the Brazilian savanna-like biome shows its typical vegetation rapidly becoming ‘cerradão’ – a biodiversity-poor forest formation – while resistance to drought and wildfires weakens. -
UNESP professor brings together accounts of journeys to inhospitable places and reflections on the future in book
2024-04-17Written by São Paulo State University’s biologist Mauro Galetti Rodrigues, A Naturalist in the Anthropocene aims to inspire young scientists and nature lovers. -
Ludo Educativo games portal surpasses 20 million views
2024-04-17Dissemination project of the Center for the Development of Functional Materials – a research center supported by FAPESP and based at the Federal University of São Carlos – is aimed at primary and secondary school students and teachers. -
Consortium including Brazilians sequences the reference genome of Arabica coffee
2024-04-17The work makes it possible to tell the story of the fusion of genomes that gave rise to the world’s most consumed species, as well as identifying genes responsible for resistance to rust and other diseases. -
FAPESP seeks to increase research collaboration with the US Midwest
2024-04-17Researchers from universities and research institutions in the State of São Paulo participate in FAPESP Week Illinois; the event aims to create new opportunities for scientific cooperation. -
Arboviruses, mosquitoes and potential hosts tracked in real time in São Paulo city
2024-04-17The technology used to sequence the first infections by SARS-CoV-2 at record speed has been successfully tested as a technique to monitor viruses transmitted by mosquitoes, such as dengue, zika, chikungunya and yellow fever. -
PROASA program will advance knowledge of South Atlantic and Antarctic
2024-04-17Launched on April 2 at FAPESP, the program will initially involve researchers from Brazil, Argentina and France. -
DNA vaccine against zika performs well in tests on mice
2024-04-17The vaccine is being developed by researchers in Brazil. The results of preclinical trials are published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology. -
Air pollution data could be used to plan better transit routes
2024-04-17Researchers from the University of São Paulo are producing maps that show areas of the city of São Paulo with the highest concentration of air pollutants; the results of the studies were presented in the United States during FAPESP Week Illinois. -
Startup develops alternative treatment for atopic dermatitis
2024-04-17Researchers supported by FAPESP have created a drug using antibodies for direct application to the skin. -
Study uses thermodynamics to describe expansion of the Universe
2024-04-15The shift from a decelerating expansion regime (in the radiation- and matter-dominated era) to an accelerating expansion regime (in the dark energy-dominated era) resembles a thermodynamic phase transition, according to an article in Results in Physics by scientists affiliated with São Paulo State University. -
Hydrogen recombination found to be most plausible explanation for high levels of energy in stellar superflares
2024-04-15The study investigated 42 superflares and concluded that this model is more consistent from the physical standpoint. -
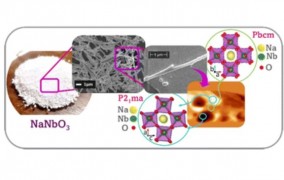
Article describes method for synthesizing material that can be used to collect and store energy
2024-04-10Sodium niobate is a type of ceramic with properties of interest to green chemistry; scientists from the Center for the Development of Functional Materials and collaborators have developed a new strategy for obtaining it. -
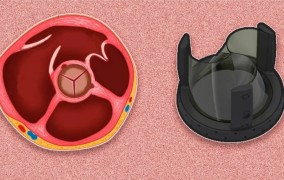
Brazilian scientists design innovative heart valve
2024-04-10Study developed at Center for Mathematical Sciences Applied to Industry aims to perfect device for cardiovascular treatments. -
French President Emannuel Macron unveils a branch of Institut Pasteur at the University of São Paulo
2024-04-10The new member of the Pasteur Network, which comprises 33 laboratories in 25 countries, is being equipped with the support of FAPESP, which is also funding several young researchers associated with the institute. -
International Research Center of France’s leading public-sector scientific research organization is unveiled at the University of São Paulo
2024-04-10FAPESP signed a memorandum of understanding to fund projects that will be conducted at the IRC. -
French Guiana joins Amazon+10 Initiative
2024-04-10An agreement to this end was signed in Belém in the Brazilian Amazon during the visit of French President Emmanuel Macron and Laurent Linguet, President of the University of French Guiana. The aim is to foster international cooperation that furthers the development of the Amazon region. -
Most patients treated by public psychiatric outpatient clinics are women aged 45 on average
2024-04-10In Brazil, researchers analyzed data for 8,384 clinical appointments that took place in a two-year period at Hospital de Base in São José do Rio Preto (São Paulo state) and found the situation to be similar to those in publicly-funded psychiatric outpatient clinics elsewhere in the country. The results, reported in Frontiers in Psychiatry, list the most common mental health problems and most frequently prescribed drugs. -
System uses artificial intelligence to detect wild animals on roads and avoid accidents
2024-04-10The researchers trained computer vision models to identify Brazilian mammals must susceptible to roadkill in real time and are partnering with toll road operators to test the system in real-world situations. -
Weight training improves symptoms of anxiety and depression in old people, study confirms
2024-04-10Brazilian researchers analyzed more than 200 articles on the subject and identified the types of training most indicated for these cases. Their findings are reported in the journal Psychiatry Research. -
Water filtration and DNA extraction help fish farmers protect animal health
2024-04-10A startup supported by FAPESP has developed a solution to prevent disease in fish tanks by means of environmental monitoring. -
Mediterranean sauté recipe induces metabolic changes that mitigate weight gain, study suggests
2024-04-03The health benefits of the so-called “sofrito” were observed in experiments with rats conducted by scientists from the Food Research Center and collaborators. The effect may be linked to a compound identified in the animals’ livers called butanediol.
Most popular
-
Amazon scorpion toxin kills breast cancer cells
2025-06-18
-
Spending more than 3 hours a day sedentary worsens teens’ mental health
2025-02-20
-
Climate change could drastically reduce aquifer recharge in Brazil
2025-09-17
-
Microplastics may affect bone health
2025-09-17
-
‘Science alone will not save us’: Paulo Jannuzzi highlights the need for republican values
2025-09-17
-
Butantan Institute says its dengue vaccine protects against serotype 3
2025-02-05
-
FAPESP aims to boost the development of quantum technologies in Brazil
2025-01-15
-
Molecule reverses cognitive deficits associated with aging and dementia in animal tests
2025-05-12
-
Ants defend plants from herbivores but can hinder pollination
2025-09-15
-
Personality traits influence the development of insomnia
2025-05-19