

In these illustrative images of Plasmodium vivax, arrows point to the asexual stages of the parasite as seen in blood smears – ring (gray), trophozoite (blue), and schizont (green) – as well as the sexual stage known as the gametocyte (red) (images: Laboratory of Tropical Diseases/UNICAMP)
As described in Scientific Reports, the study involved analysis of blood samples from volunteers infected by Plasmodium vivax, which produces forms that lie dormant in the host and can be reactivated months after treatment. The findings will help detect and diagnose these forms, with significant potential to enhance control and treatment of the disease in future.
As described in Scientific Reports, the study involved analysis of blood samples from volunteers infected by Plasmodium vivax, which produces forms that lie dormant in the host and can be reactivated months after treatment. The findings will help detect and diagnose these forms, with significant potential to enhance control and treatment of the disease in future.
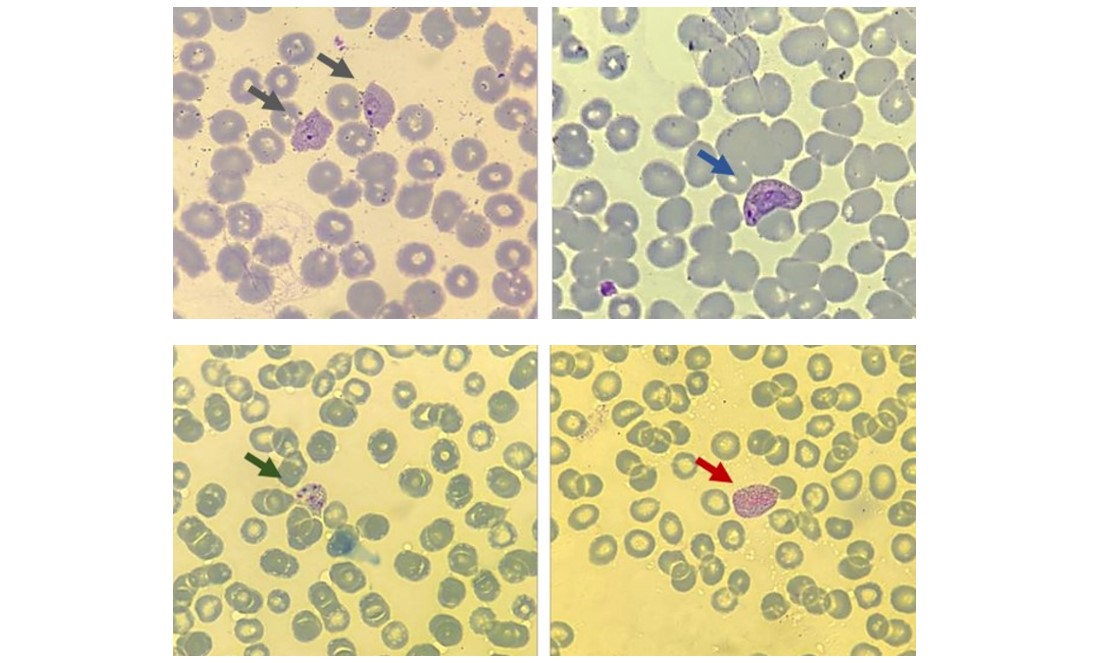
In these illustrative images of Plasmodium vivax, arrows point to the asexual stages of the parasite as seen in blood smears – ring (gray), trophozoite (blue), and schizont (green) – as well as the sexual stage known as the gametocyte (red) (images: Laboratory of Tropical Diseases/UNICAMP)
By Julia Moióli | Agência FAPESP – The most common type of malaria in Brazil is caused by the parasite Plasmodium vivax. Although vivax malaria is milder than the variant caused by P. falciparum, the ability of P. vivax to produce dormant forms in the host’s liver that can be reactivated months after the end of treatment makes it very hard to control. According to the scientific literature, such recurrence may account for some 90% of cases in Brazil.
In an article published in the journal Scientific Reports, Brazilian researchers describe for the first time possible biomarkers associated with recurrence of vivax malaria.
Funded by FAPESP (projects 17/18611-7 and 21/04632-8), the research is bringing to light significant information about potential targets for the development of antimalarial drugs and possible markers relating to the risk of recurrence.
As the authors explain, recurrence is a newly detectable episode after treatment for a previous episode and may arise from relapse, reinfection or recrudescence (reappearance of parasite forms in the bloodstream after they have been treated to undetectable levels for a period).
In the study, researchers at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), the State University of Amazonas (UEA) and the Federal University of Goiás (UFG) analyzed blood plasma samples from 110 patients who lived in the Amazon region; 51 had recurring vivax malaria and 59 were still suffering from their first episode. The samples were submitted to a technique known as untargeted metabolomics, entailing a comprehensive analysis of all the metabolites they contained. The aim was to understand how the patients’ metabolisms were affected during the first episode in comparison with recurrent cases.
The patients were monitored for 180 days. A majority had a “new” episode between 40 and 60 days after the first. Analysis by mass spectrometry to identify compounds based on molecular mass revealed 52 and 37 significant metabolites in the participants with recurrent and non-recurrent malaria respectively.
“Overexpression of metabolites was typical in the initial episode, whereas recurrent episodes were characterized by a larger number of diminished metabolites,” Jessica R. S. Alves, a researcher at UNICAMP’s Institute of Biology and a co-author of the article, told Agência FAPESP.
“Furthermore, the patients with recurrence were found to exhibit modulation above all in lipid pathways involved in production of prostaglandin and leukotriene – molecules that play key roles in the host’s immune system. The first-episode group exhibited alterations in their tryptophane and vitamin B6 [pyridoxine] metabolisms, described in the literature as being important nutrients in the host that the parasite uses to develop.”
An in-depth analysis of selected datasets relating to recurrent malaria also pointed to an enrichment of other metabolic pathways, including those for butanoate, aspartate, asparagine and N-glycan.
“All these markers suggest pathways associated with recurrence and can be used in future to characterize it,” said Gisely C. de Melo, a researcher at UEA and co-corresponding author of the article.
Prospects
“The paper’s main contribution lies in directing the analysis to identification of the metabolic pathways that must be investigated in greater detail in order for us to understand and fill in the gaps in the study of recurrence,” said Fabio Trindade Maranhão Costa, a professor at IB-UNICAMP and a co-author of the article.
Two limitations of the study are acknowledged by the authors: the relatively small number of participants, and uncertainty as to whether the recurrences were relapses or new infections.
“At this time, we have no way of diagnosing relapses and treating them appropriately,” Melo said.
According to the authors, next steps include multicenter trials involving a larger number of patients and wider geographical coverage. They also plan to compare plasma metabolomics with urinary or saliva metabolomics in non-recurrent, recurrent and relapsing vivax malaria; analyze lipidomes, proteomes, transcriptomes and genomes; and explore the immune profiles of patients with and without recurrence.
In addition to FAPESP’s support, the study was funded by Brazil’s National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), The World Academy of Science (TWAS), the Amazonas State Research Foundation (FAPEAM), and Instituto Serrapilheira.
The article “Host metabolomic responses in recurrent P. vivax malaria” is at: www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-54231-5.
Republish
The Agency FAPESP licenses news via Creative Commons (CC-BY-NC-ND) so that they can be republished free of charge and in a simple way by other digital or printed vehicles. Agência FAPESP must be credited as the source of the content being republished and the name of the reporter (if any) must be attributed. Using the HMTL button below allows compliance with these rules, detailed in Digital Republishing Policy FAPESP.





