Search: 4362 news
-
Project combines data science and sociology to map crime
2024-04-03With the support of FAPESP, the research is developing mathematical and computational tools that will address issues related to public safety in an innovative way. -
Database maps São Paulo’s bus corridors
2024-04-03Center for Metropolitan Studies research covers nearly 200 kilometers of roads in the Metropolitan Region. -
Innovative molecular biology technique allows for discovery of novel targets for candidate vaccines against schistosomiasis
2024-04-03Experiments conducted at Butantan Institute in São Paulo used phage display to screen 12,000 proteins found in Schistosoma mansoni, the worm that causes the disease. The method deployed bacteriophages, viruses that infect bacteria, to identify key parasite peptides. -
In the remote past, the Amazon had large cities connected by roads
2024-04-03This was the subject of the second FAPESP Lecture 2024, delivered by archeologist Eduardo Neves, one of the leading proponents of the major revision that changed the way researchers think about the Amazon’s past. -
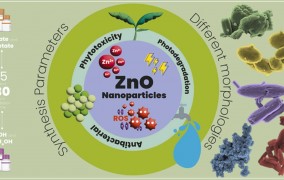
Study describes strategy for inactivation of multidrug-resistant bacteria
2024-04-03Zinc oxide nanoparticles with varying morphologies were tested against microorganisms isolated from patients. The results are reported in the Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. -
Genetic improvement of conventional soybeans generates special varieties
2024-04-03A startup supported by FAPESP is developing novel cultivars to offer growers a high-value-added option. -
Dengue-bearing mosquito and other invasive species in Brazil cause annual losses of up to BRL 15 billion
2024-04-03The number may be an underestimate in light of gaps in studies of the problem, according to the authors of a report issued by the Brazilian Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. -
Amphibians use scream inaudible to humans for self-defense against predators, study suggests
2024-04-03For the first time in South America, researchers recorded the use of ultrasound by a frog endemic to the Atlantic Rainforest in Brazil, which has more species of amphibians than any other country. Other frogs may use very high-frequency calls for the same purpose. -
University of Illinois plans new model for research collaboration with Brazil
2024-04-03The Brasillinois program, which will be launched this month during FAPESP Week Illinois in the United States, aims to promote student and faculty mobility and foster connections in areas such as climate and sustainability, medicine, public health, and social inclusion. -
Group proposes research protocol to regularize artisanal cheeses
2024-03-27The proposal is being analyzed by an inspection body in the state of São Paulo. In this region alone, there are more than 1,200 informal producers of milk and dairy products with the potential to be regularized. -
Group obtains patent for method to create more natural, effective and environmentally friendly sunscreens
2024-03-27Developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo, the process proposes using silica particles coated with melanin in formulations to protect the skin not only from UVA and UVB rays, but also from visible light. -
Innovation in genome editing of tropical maize could accelerate agricultural research in the country
2024-03-27Three of the five tropical strains were successfully transformed using the morphogenic gene expression strategy, achieving efficiency rates three times higher than the average of the protocols. -
Chile-Brazil collaboration is studying impact of climate change in one of the world’s most untouched places
2024-03-27Working in partnership with scientists at the University of Magallanes in Chile, Brazilian researchers are conducting studies of the Chilean subantarctic region. -
Science20 Brazil emphasizes importance of science to global transformation
2024-03-27Representatives of science academies in 19 countries and organizations in Brazil and elsewhere assembled in Rio de Janeiro to begin producing documents and recommendations on science, technology and innovation for the G20 summit in November. -
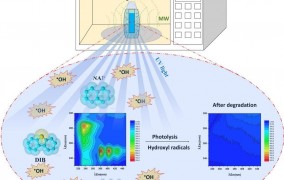
Researchers obtain promising results for control of pollutants in water
2024-03-27Brazilian scientists tested a simple and sustainable method for monitoring and degrading a mixture of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, compounds present in fossil fuels and industrial waste. -
Protein created by Brazilian startup could help treat diseases caused by HPV
2024-03-27Developed by ImunoTera as part of a project supported by FAPESP, the molecule triggers the immune system’s response to infected cells and helps combat the disease. -
Spanish public-sector R&D enterprise and FAPESP sign memorandum of understanding for ST&I cooperation
2024-03-27Pedro Sánchez, Prime Minister of Spain, was present at the ceremony in São Paulo where the MoU was signed by the Spanish ambassador to Brazil and the President of FAPESP. -
Study reveals evidence of violence at a time of crisis in ancient Peru
2024-03-27Analysis of skeletons exhumed at a burial ground dating from the period 500-400 BCE, shortly after the collapse of the Chavín culture, revealed lethal injuries inflicted on men, women and children, as well as signs of material poverty. -
RCGI joins international consortium to coordinate collaboration on zero-carbon initiatives
2024-03-20The Global Technology Hub, launched at COP28, will promote decarbonization projects and financing. The goal is to enable developing countries to achieve net-zero emissions. -
World’s largest epilepsy study reveals ‘genetic architecture’ and points to new therapies
2024-03-20More than 29 thousand patients were analyzed and 26 areas of the genome associated with the disorder were identified; Brazil was the only Latin American representative through the Brazilian Institute of Neuroscience and Neurotechnology of the State University of Campinas. -
Brazilian study is the most read in the Physchem journal in 2022
2024-03-20A paper by scientists from the Center for the Development of Functional Materials discusses the effects of femtosecond laser irradiation, which can create and functionalize new materials for the microelectronics industry. -
Scientists develop catalyst designed to make ammonia production more sustainable
2024-03-20Created at a FAPESP-supported research center, the material helps produce ammonia by electrochemical reduction of nitrogen gas, dispensing with the high temperature and pressure required by the conventional method. -
Study maps main genes involved in immune response to infection by dengue virus
2024-03-20Researchers at the University of São Paulo in Brazil compared data for the immune response induced by natural infection and vaccines. They identified the key factors in the development of long-lasting immunity. Their findings can be used to develop novel vaccines and antiviral therapies. -
Study shows how to improve management of municipal solid waste
2024-03-20Researchers analyzed solutions implemented in four very different Brazilian cities. Based on the results, they propose creation of a national carbon credit fund to support sustainable waste management initiatives. -
A new São Paulo School of Advanced Science at the Brazilian Center for Research in Energy and Materials is receiving applications
2024-03-20SyncLight 2024 will discuss the recent opportunities offered by advanced experimental synchrotron techniques available at Sirius, the Brazilian 4th generation light source. -
Study clarifies a key question in particle physics
2024-03-20The researchers identified the origin of discrepancies in recent predictions of the muon’s magnetic moment. Their findings could contribute to the investigation of dark matter and other aspects of the new physics. -
Sandy soil reptiles are more threatened by climate change than has been supposed, study shows
2024-03-20An analysis of occurrence records for ten lizard and snake species found in three South American biomes – the Caatinga and Cerrado in Brazil and the Chaco in Argentina and Paraguay – showed that rising temperatures in the coming decades could lead to extinction in some cases and drastic habitat loss in others. The authors advocate an increase in full-protection conservation units suited to these animals. -
Artificial intelligence enhances inspection in poultry processing industry
2024-03-20The system created by startup Ecotrace with FAPESP’s support is designed to help poultry processors detect carcass lesions in real time. -
How a government program promoted conservation of Atlantic Rainforest remnants on rural properties
2024-03-13Farmers in the Paraíba Valley region of São Paulo state received economic incentives such as payment for environmental services to adopt conservation practices and protect native vegetation. -
Wood condition, root constriction and improper pruning can be used as predictors of urban tree failure
2024-03-13A study of the São Paulo city center in Brazil proposed guidelines and specified stakeholder roles for reducing the number of tree failures, which average 2,000 per year there.
Most popular
-
Amazon scorpion toxin kills breast cancer cells
2025-06-18
-
Spending more than 3 hours a day sedentary worsens teens’ mental health
2025-02-20
-
Climate change could drastically reduce aquifer recharge in Brazil
2025-09-17
-
Microplastics may affect bone health
2025-09-17
-
‘Science alone will not save us’: Paulo Jannuzzi highlights the need for republican values
2025-09-17
-
Butantan Institute says its dengue vaccine protects against serotype 3
2025-02-05
-
FAPESP aims to boost the development of quantum technologies in Brazil
2025-01-15
-
Molecule reverses cognitive deficits associated with aging and dementia in animal tests
2025-05-12
-
Ants defend plants from herbivores but can hinder pollination
2025-09-15
-
Personality traits influence the development of insomnia
2025-05-19